

Protection (e.g., vertebrae protect the spinal cord).Include the sacrum, coccyx, vertebrae, mandible, palatine, hyoid, and temporal bones.Function to reduce friction of the tendon and to reduce excessive wear.Bones that develop within tendons (e.g., the patella).Composed of two layers of compact bone that surrounds trabecular bone and bone marrow.Include the scapulae, sternum, ribs, and most bones of the skull.Short bones: include tarsal and carpal bones.Apophysis: large bony projections where ligaments and tendons attach.Consists of compact bone and the medullary cavity where the bone marrow is stored.Metaphysis: area between the epiphysis and the diaphysis.Contains the articular surface of bones.
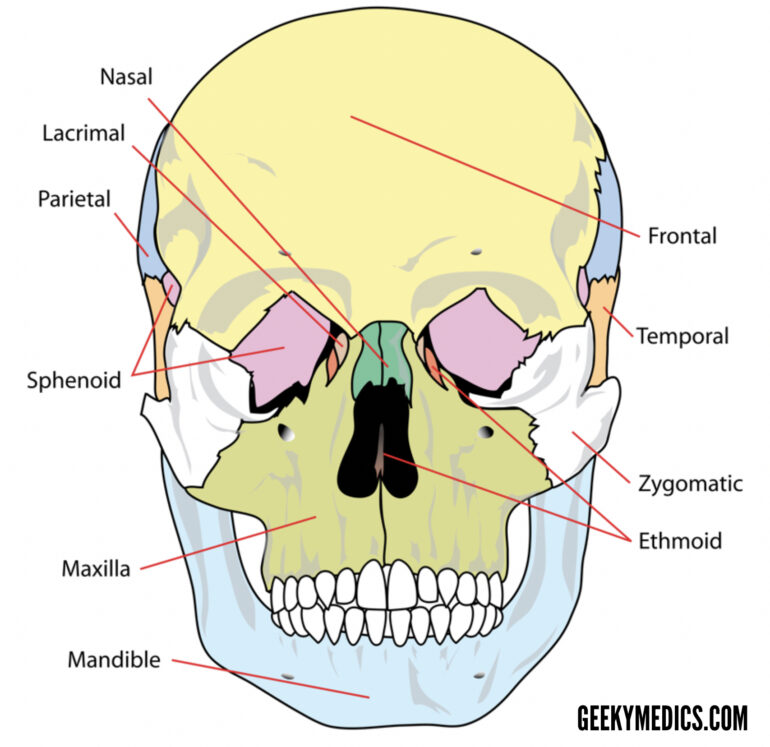
Long bones : include the femur, humerus, ulna, radius, fibula, tibia, metacarpals, and phalanges.Storage ( calcium and phosphorus reservoir).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
